Production Format
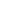
Antibodies are composed of 4 chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The heavy chains are roughly twice the size of the light chains. A heavy chain contains one variable domain (VH) and three constant domains (CH1, CH2 and CH3). In contrast, a light chain contains only one variable domain (VL) and one constant domain (CL).
For recognition of an epitope on a given target (i.e. the antigen), the important antibody regions are the variable domains (VH and VL). Together, they are referred to as the Fv region, or the antigen-binding site.
The constant domains form the Fc region. This region also defines the different antibody isotypes: IgA, IgE, IgM, IgG. Inside an organism, this region is responsible for modulating immune cell activity. The Fc part is the part recognized by secondary reagents, when performing classical immunodetection (ELISA, immunofluorescence, western blots...).
Recombinant antibodies can be engineered in several different formats, other than classical IgG molecules.
The standard format of the custom-made ABCD antibodies is a mini-antibody, with the single chain Fv antigen-binding domain (scFv) fused to an Fc domain (scFv-Fc). The Fc portions can be rabbit IgG, human IgG1 and IgG2, mouse IgG1 and IgG2, or guinea pig IgG.
For all practical purposes, a mini-antibody is essentially used as a standard IgG antibody and can be used with all standard secondary reagents that recognize the constant Fc domain.
Other formats are also possible, such as: full IgG molecule, different isotypes (IgA or IgM), chromobodies (the scFv domain fused to a reporter protein, such as GFP).
We deliver 50-100 μg of non-purified cell supernatant (+0.02% sodium azide) produced in HEK293 suspension cells, growing in serum-free medium, transiently transfected with the expression vector coding for the antibody.
ABCD Antibodies cannot produce antibodies protected by active patents.